Setting usage limits
As an administrator, you can set usage limits for crucial resources such as Metered RAM, Metered RAM hours, and storage.
For a description of these types of usage, see How usage is calculated.
Contents
Usage limits overview
Kyndryl Cloud Uplift monitors four types of usage: storage The amount of data storage space used by assets, environments, and templates. , Metered RAM hours A unit of measurement that corresponds to the total number of hours that your account has run VMs, translated into their Metered RAM equivalents. 1 Metered RAM hour is equivalent to 1 GB of Metered RAM running for 1 hour. To learn more, see How usage is calculated. , concurrent VMs The number of VMs running simultaneously. To learn more, see How usage is calculated. , and concurrent Metered RAM The amount of RAM in use for all simultaneously running VMs. To learn more, see How usage is calculated. . If Power A CPU architecture that supports IBM i, AIX, and Linux (on Power) in Kyndryl Cloud Uplift. VMs are enabled for your account, Metered RAM hours and Concurrent Metered RAM are tracked separately for x86 The most common CPU architecture. x86 CPUs support Windows and Linux VMs in Kyndryl Cloud Uplift. and Power A CPU architecture that supports IBM i, AIX, and Linux (on Power) in Kyndryl Cloud Uplift. VMs.
Each type of usage is monitored (and can be limited) at various levels within your account:
| Limit | Description |
|---|---|
| User limits (optional) for storage, Metered RAM hours, concurrent VMs, and Concurrent Metered RAM |
These limits control usage associated with the environments, templates, and assets that a specific user owns. If an environment is shared with multiple users, usage is tracked against the environment owner. For example, if Jim runs a VM in an environment that Julie owns, the concurrent VMs, concurrent Metered RAM and Metered RAM hours are tracked against Julie’s user limits, not Jim’s. The storage usage for the environment is also tracked against Julie’s user limit. For instructions, see Setting department usage limits. |
| Department limits (optional) for storage, Metered RAM hours, concurrent VMs, and Concurrent Metered RAM |
These limits control the usage associated with the environments, templates, and assets owned by all of the users in a department. For instructions, see Setting department usage limits. |
| Regional limits for storage and Concurrent Metered RAM |
These limits control the maximum Concurrent Metered RAM and storage usage consumed by the environments, templates, and assets in a specific region. If your account doesn’t have regional limits, Concurrent Metered RAM and storage are instead controlled at the account-wide, global level. For instructions, see Setting global and regional limits. |
| Account-wide, global limits for Metered RAM hours and concurrent VMs |
These limits control the cumulative Metered RAM hours and maximum concurrent VMs for all environments in the account. For instructions, see Setting global and regional limits. |
When a user is subject to multiple limits for the same type of usage (for example, a regional storage limit, a department storage limit, and a user storage limit), the user’s usage is halted when any of those limits are met. For example, if the regional storage limit has been met, then users can’t create any more resources in that region, even if they have remaining usage left in their department and user limits.
How different usage limits interact
If Julie has a user storage limit of 25 GB, Julie’s department has a storage limit of 250 GB, and the company has a storage limit of 1 TB:
- Julie won’t be able to exceed her limit of 25 GB, even though her department allows up to 250 GB.
- If Julie has a special need, the administrator may remove her user storage limit, which would let her use all 250 GB of the department’s storage. While Julie is using all of the department’s storage, no one else in the department can use any storage, even if their individual limits haven’t been met.
- 750 GB remains reserved for use by other departments.
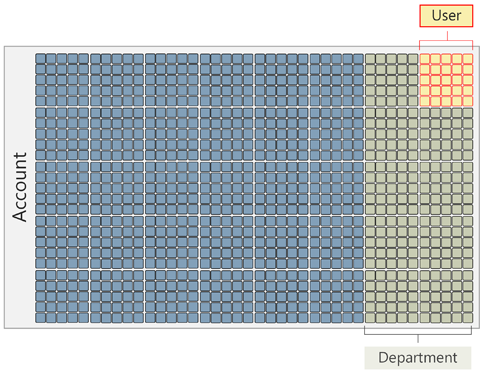
To guarantee all the users in a department have access to resources, set the limits of all other departments and user accounts such that the sum total of their limits is below the overall company limit. This creates a gap between their combined limits and the company limits that ensures that resources are available for your department.
How usage is restricted when a limit is reached
Kyndryl Cloud Uplift automatically prevents users from taking actions that would exceed a limit (such as creating a template or running VMs). When a limit is reached, the user, department, or account encounters the following:
- RAM Hours – All running VMs are suspended. You can’t use more Metered RAM hours unless you increase the user, department, or account limit.
- RAM or VM limit – No more VMs can be started. Stop running VMs to release Metered RAM and VMs and allow more to be started.
- Storage – No more templates or environments may be created. Delete templates or environments to allow more to be created.
Instructions
Setting usage limits for users
You must be an administrator or user manager to edit user limits. User managers can’t edit limits for an administrator’s account.
To set or edit a user’s limits
-
Navigate to Manage > Users.
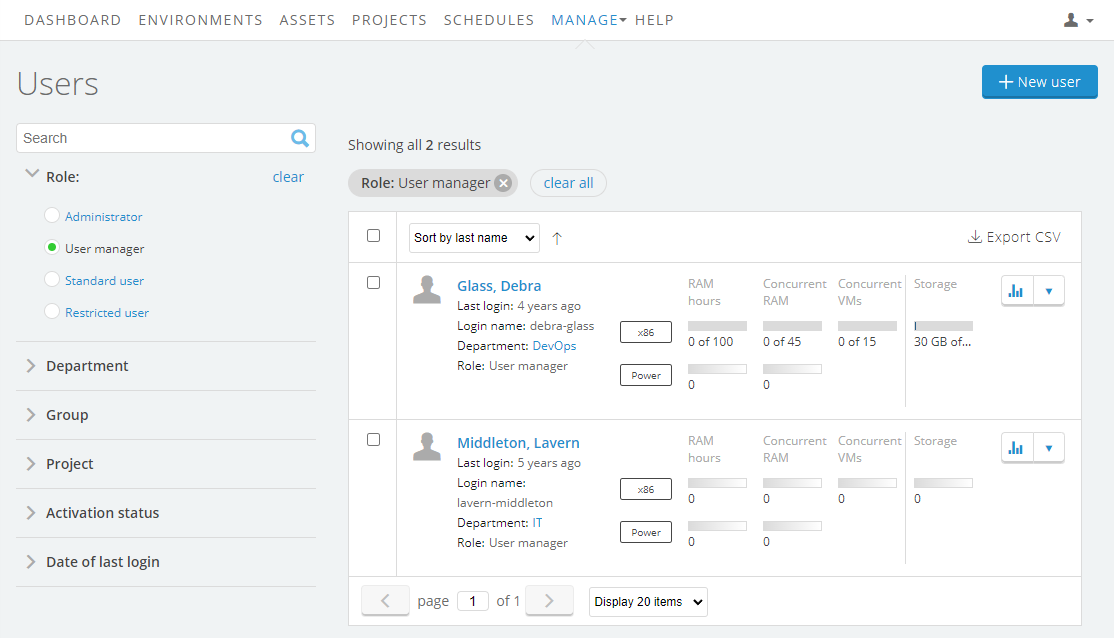
-
Click
 (Edit User Limits) next to the user you want to edit.
(Edit User Limits) next to the user you want to edit.To set usage limits for multiple users
- On the Users page, click Select.
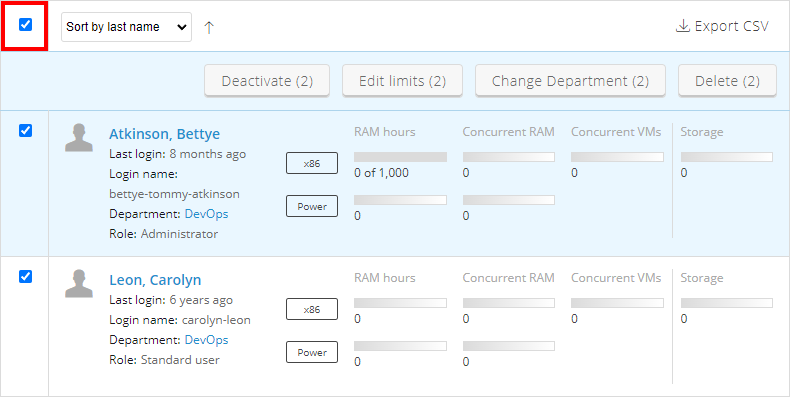
- Select the users you want to edit.
- Click Edit limits. The Edit User Limits window displays.
- On the Users page, click Select.
-
In the Edit User Limits window, enter a Storage (choose GB or TB), RAM hours, Concurrent VMs, and/or Concurrent RAM limit. To set no limit, select Use max. When Use max is selected, the user can use up to the account limit for the billing period. The user’s department limit (if applicable) is displayed in the Max: field.
If Power VMs are enabled for your account, you set Concurrent RAM limits for x86 and Power individually.
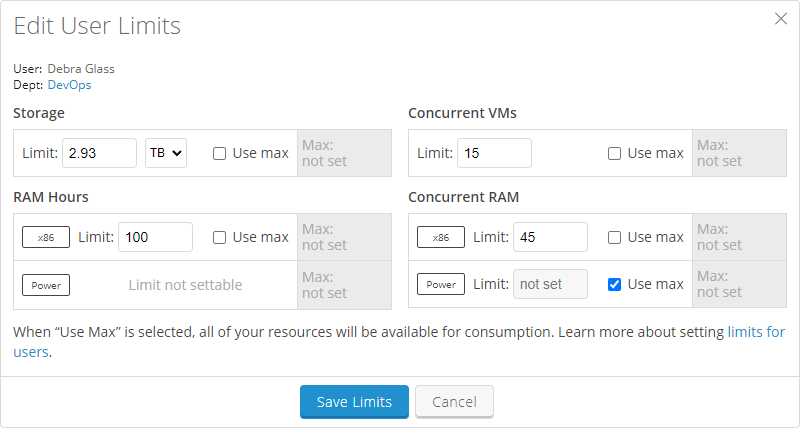
A user’s limit can be set higher than the department, regional, or account limit. The sum of all user limits doesn’t need to equal the department, regional, or company limit. However, the user’s actual usage can’t exceed the department, regional, or company limit.
-
Click
 (Save Limits).
(Save Limits).
Setting department usage limits
Administrators can also track and control usage on a departmental basis.
To set a department limit
-
Click Manage > Departments.
The Departments page displays.
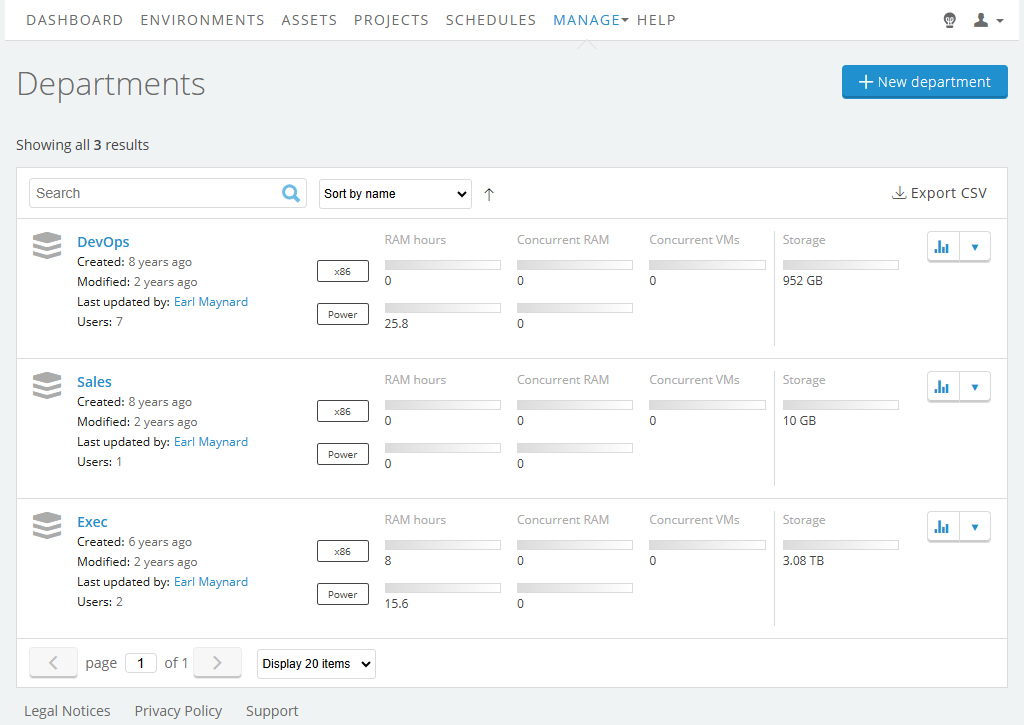
- Click
 (Edit limit) next to the department you want to edit.
(Edit limit) next to the department you want to edit. -
In the Edit Department Limits window, enter a Storage (in GB), RAM hours, Concurrent VMs, and/or Concurrent RAM limit. To set no limit, select Use max. When Use max is selected, the department can use up to the account limit for the billing period; the account limit is displayed in the Max: field.
If Power VMs are enabled for your account, you set Concurrent RAM limits for x86 and Power individually.
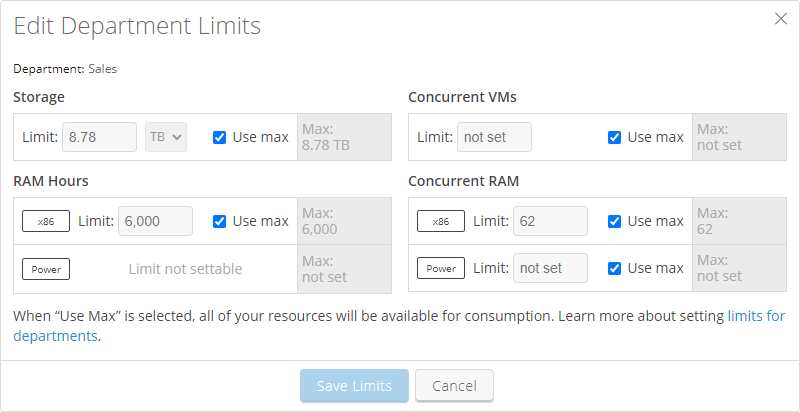
- Click Save Limits.
Setting global and regional limits
To edit global limits
- Navigate to the Manage > Usage & Limits page.

-
In the Usage & Limits: Global section, click Edit for the parameter you want to change.
The parameter dialog displays.
- Set Enable pay-as-you-go limits to On
-
Type a value for Limit, which is the total usage limit available when burst is enabled.
Notes
- The value for Limit A hard cap placed on a user, department, or customer account usage of storage, RAM hours, concurrent Metered RAM, and concurrent VMs. Limits may apply to global usage or to usage in a particular region. To learn more, see Usage limits overview. must be between the reserved capacity The global or regional limit for concurrent RAM, RAM hours, storage (GB), networks, and public IP addresses defined in your contract. You can exceed your account reserved capacity by setting a higher limit for max concurrent Metered RAM, Metered RAM hours, and storage usage. You are charged a premium for this additional usage. limit and the Max settable limit The highest usage limit that you can set for your account. To increase this value, contact support. .
- By setting a limit that is higher than your reserved capacity, you can enable pay-as-you-go Any usage of maximum concurrent RAM, cumulative RAM hours, or overall storage capacity in excess of your reserved capacity, globally or in any region. To learn more, see Current account usage overview. , which allows your users to work on business-critical projects even after you exceed your expected billing rate.
- For more information about limits and pay-as-you-go, see Understanding pay-as-you-go.
To edit regional limits
- Navigate to the Manage > Usage & Limits page.
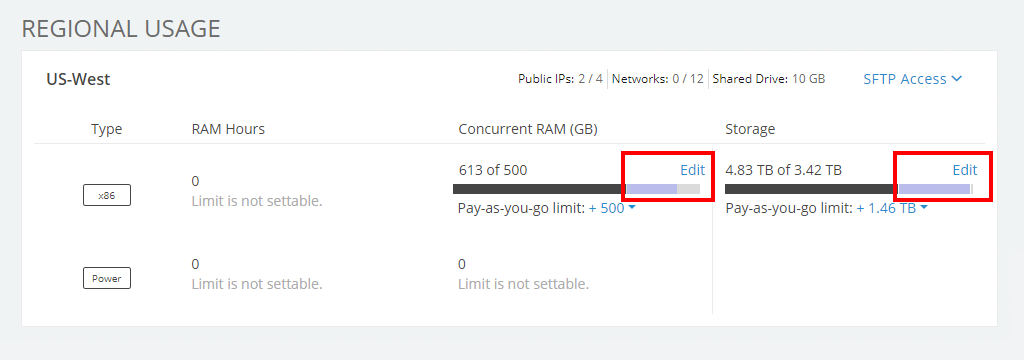
-
In the Usage & Limits: Regional section for the region you want to edit, click Edit for the parameter you want to change.
The parameter dialog displays.
- Set Enable pay-as-you-go limits to On

-
Type a value for Limit, which is the total usage limit available when burst is enabled.
Notes
- The value for Limit A hard cap placed on a user, department, or customer account usage of storage, RAM hours, concurrent Metered RAM, and concurrent VMs. Limits may apply to global usage or to usage in a particular region. To learn more, see Usage limits overview. must be between the reserved capacity The global or regional limit for concurrent RAM, RAM hours, storage (GB), networks, and public IP addresses defined in your contract. You can exceed your account reserved capacity by setting a higher limit for max concurrent Metered RAM, Metered RAM hours, and storage usage. You are charged a premium for this additional usage. limit and the Max settable limit The highest usage limit that you can set for your account. To increase this value, contact support. .
- By setting a limit that is higher than your reserved capacity, you can enable pay-as-you-go Any usage of maximum concurrent RAM, cumulative RAM hours, or overall storage capacity in excess of your reserved capacity, globally or in any region. To learn more, see Current account usage overview. , which allows your users to work on business-critical projects even after you exceed your expected billing rate.
- For more information about limits and pay-as-you-go, see Understanding pay-as-you-go.
