Overview of VPNs
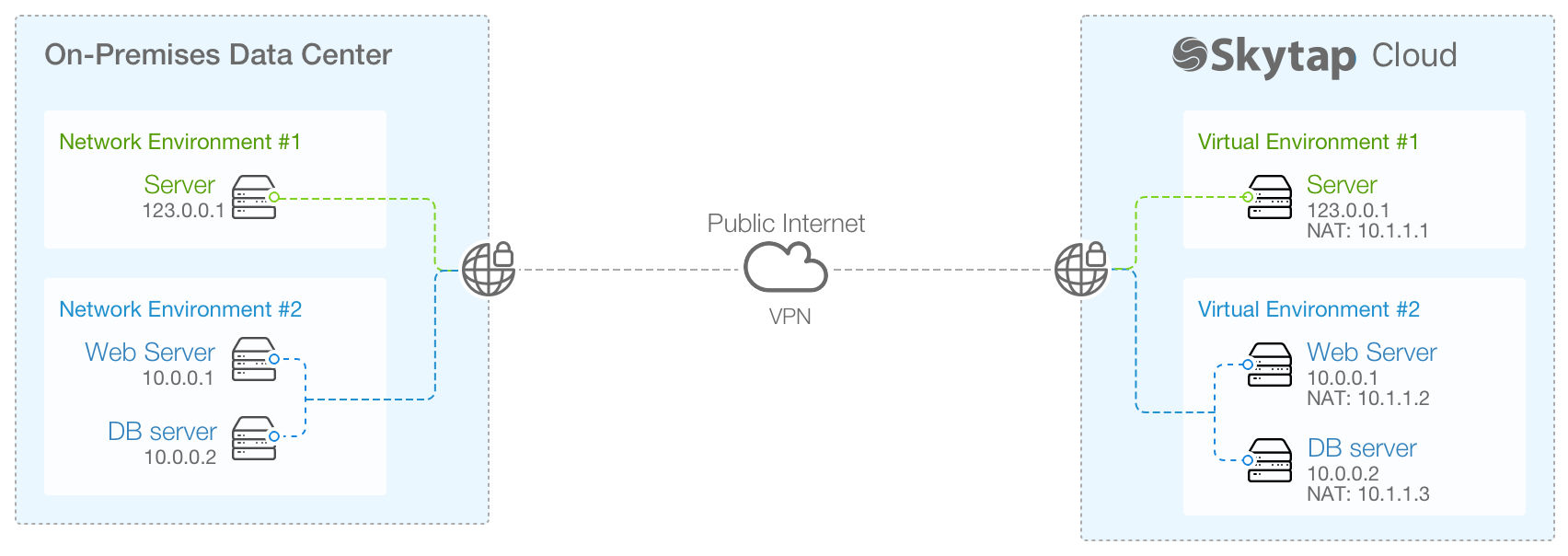
Kyndryl Cloud Uplift VPNs securely send network traffic between an external network (such as a network in your on-premises data center or another cloud service provider) and one or more Kyndryl Cloud Uplift virtual environments in your account.
Each VPN:
- Uses a Kyndryl Cloud Uplift virtual network endpoint to route traffic between an external network and one or more virtual environments in a Kyndryl Cloud Uplift region.
- Has granular access controls that let administrators decide which users, groups, and departments can attach virtual environments to the VPN.
- Can optionally be configured to use Network Address Translation (NAT). NAT assigns additional, unique IP addresses to virtual machines attached to the VPN. This means that cloned Kyndryl Cloud Uplift environments can be attached to the same network without IP address conflicts.
VPN traffic passes securely through the public Internet.
Example diagram
Best for
- Connections between Kyndryl Cloud Uplift and:
- Smaller corporate offices or data centers.
- Other cloud service providers.
Requirements
- You must have a network appliance that is accessible from the public Internet.
- Your Kyndryl Cloud Uplift account must be enabled for VPNs (most accounts are).
To get started
-
Work with your IT organization to gather the configuration parameters for the network appliance you want to connect to.
Then, use the WANs page in your Kyndryl Cloud Uplift account to create the VPN connection.
