Enabling promiscuous mode on a network adapter
Promiscuous mode allows a VM network adapter to transmit traffic using a forged MAC address. By default, promiscuous mode is disabled across your account for all network adapters.
Promiscuous mode isn’t available for Power A CPU architecture that supports IBM i, AIX, and Linux (on Power) in Kyndryl Cloud Uplift. VMs.
Contents
Overview
A network adapter uses its MAC address to label outgoing network traffic and identify incoming network traffic. Generally, the network adapter only accepts network packets that include the network adapter MAC address; traffic for other devices is dropped.
Promiscuous mode allows a network adapter to transmit network packets with other source MAC addresses. This is useful for applications like load balancers and transparent proxies.
Notes
- Promiscuous mode should not be confused with port mirroring or span ports, where a network switch can send a copy of all traffic in a particular network to a particular port on another network.
- Network adapters with promiscuous mode can't accept unicast traffic intended for other VMs or traffic between other VMs within the same network.
- Because Kyndryl Cloud Uplift sends traffic only to network adapters that actively use a specific MAC address, promiscuous mode doesn't allow passive observation of network traffic.
Requesting the promiscuous mode option for a customer account
By default, promiscuous mode is disabled on all network adapters, and the user permission associated with promiscuous mode is hidden. To request the use of promiscuous mode in your account, contact support@skytap.com.
Promiscuous mode requests must be approved by Kyndryl Cloud Uplift and can take up to two weeks to complete. To speed up the process, please include a detailed description of how you intend to use promiscuous mode. If possible, provide a simple network diagram.
Administrators: To check if promiscuous mode is enabled for your customer account, navigate to Manage > Users and click on your own user account name to view your user account details. If the promiscuous mode permission option is visible in the permissions list, this feature is enabled.

Editing promiscuous mode permissions for user and administrator accounts
Once the promiscuous mode option is enabled, Kyndryl Cloud Uplift exposes a promiscuous mode permission setting on each user and administrator user account. By default, this permission is disabled for all users, including the administrator.
-
Administrators can allow a user or administrator to use promiscuous mode by editing the user account settings.
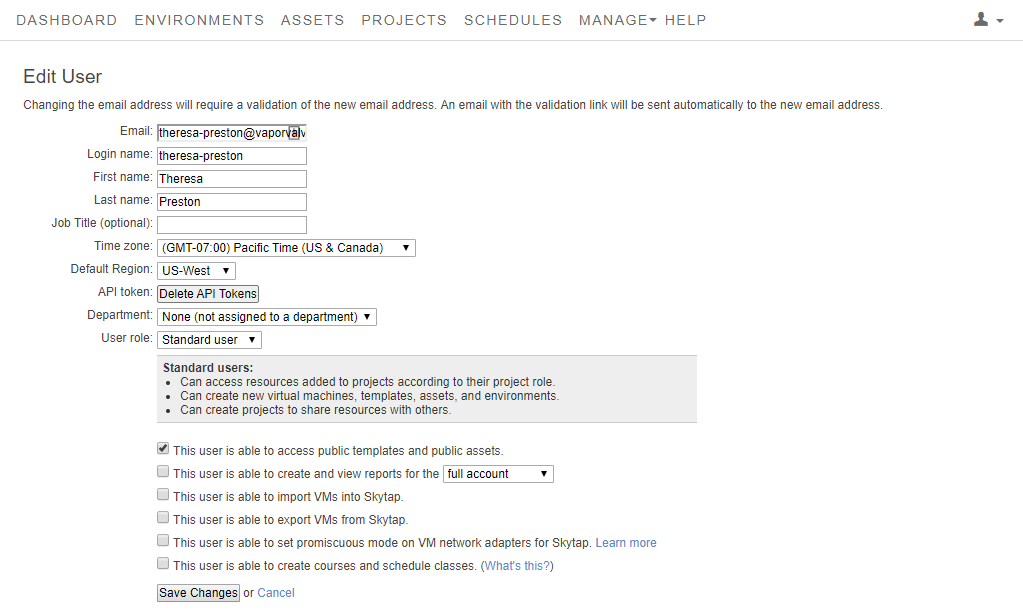
For instructions about editing an account, see Managing users and permissions.
-
If the promiscuous mode option isn’t available, contact support@skytap.com to enable this feature.
Enabling and disabling promiscuous mode for a network adapter
Users and administrators with promiscuous mode permissions can enable this setting on VM network adapters.
To edit the promiscuous mode setting for a VM network adapter
-
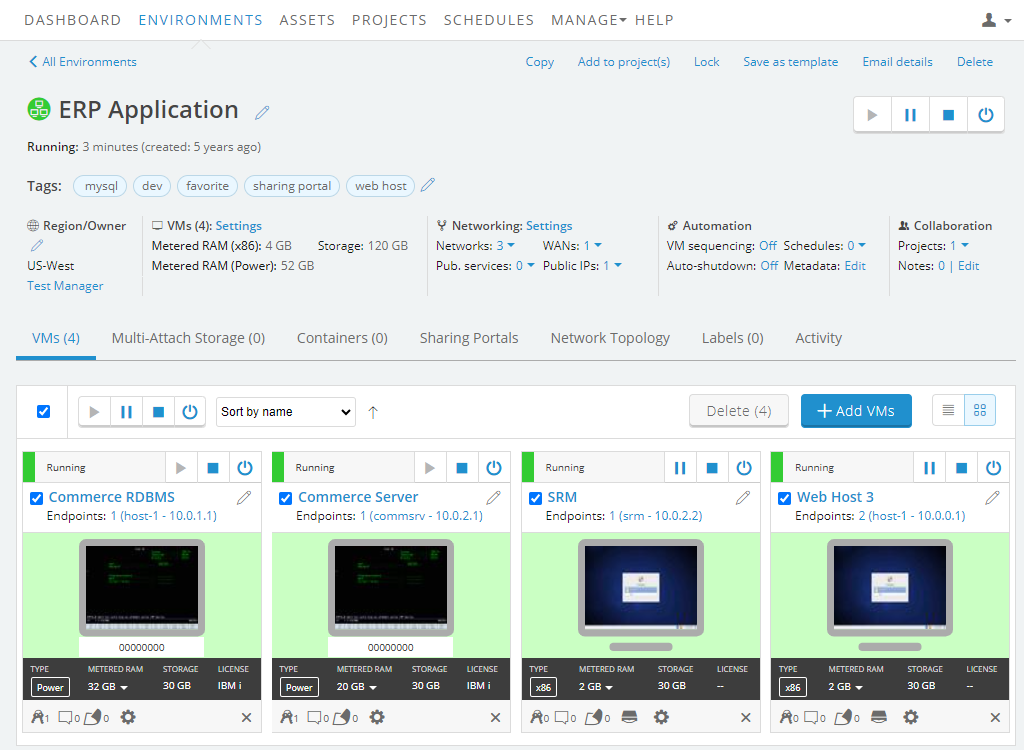
Navigate to the VM Settings > Network Adapters page for the VM you want to edit.
-
Navigate to the environment.
-
Click
 (Settings) for the VM you want to edit.
(Settings) for the VM you want to edit.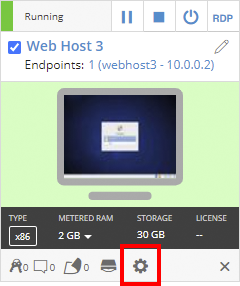
If the Settings button isn’t visible, you don’t have permission to edit the VM settings. Work with your instructor or Kyndryl Cloud Uplift administrator to edit these settings.
-
The VM Settings page displays. Click the Network Adapters tab.
-
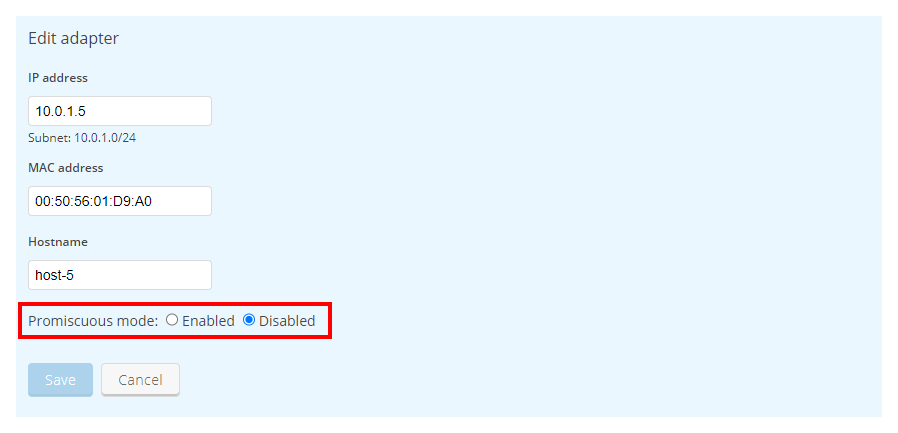
- For the network adapter you want to edit, click Edit.
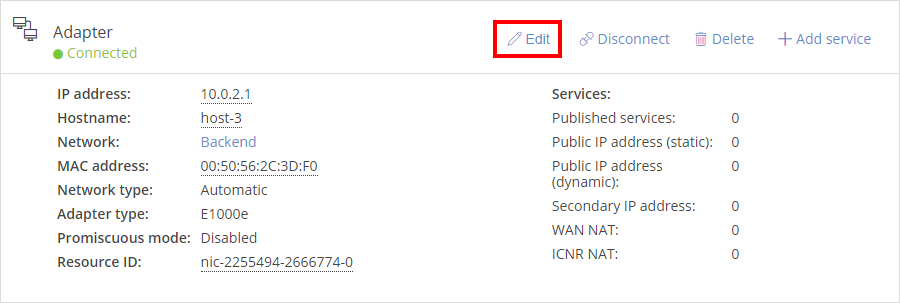
- Next to Promiscuous mode, select Enabled, and then click Save. The network adapter is now set for promiscuous mode. You can disable promiscuous mode at any time by selecting Disabled from the same window.
Notes
- Promiscuous mode can only be enabled once per VM per network. If a VM has multiple network adapters attached to the same network, only one of these network adapters can have promiscuous mode enabled.
- If you don't have permission to edit the promiscuous mode settings, this field is read-only. If this field doesn't appear, promiscuous mode is disabled and you don't have permission to edit it. Contact your administrator to enable this permission (to find your account administrator, see Finding your primary administrator).
