Managing individual containers
After you’ve added containers to a container host, you can rename a container, change the run state of each container individually, view details about each container, and delete containers.
The following commands are available for each container:
 (Rename this container) – Change the name of this container.
(Rename this container) – Change the name of this container.
 (Start/Unpause this container) – Start a container or resume this container.
(Start/Unpause this container) – Start a container or resume this container.
 (Pause this container) – Pause this container.
(Pause this container) – Pause this container.
 (Stop this container) – Gracefully stop this container
(Stop this container) – Gracefully stop this container
 (More options) – Shows a drop-down menu with additional options for this container:
(More options) – Shows a drop-down menu with additional options for this container:
 (Restart) – Stop and re-run this container.
(Restart) – Stop and re-run this container.
 (Kill) – Abruptly force stop this container.
(Kill) – Abruptly force stop this container.
 (View log) – View the most recent entries to the log file for this container.
(View log) – View the most recent entries to the log file for this container.
For more information about what information is logged, see docker logs.
 (Delete) – Delete this container from the container host.
(Delete) – Delete this container from the container host.
The container summary page
The container summary page displays detailed information about a container and provides controls to change the run state of the container.
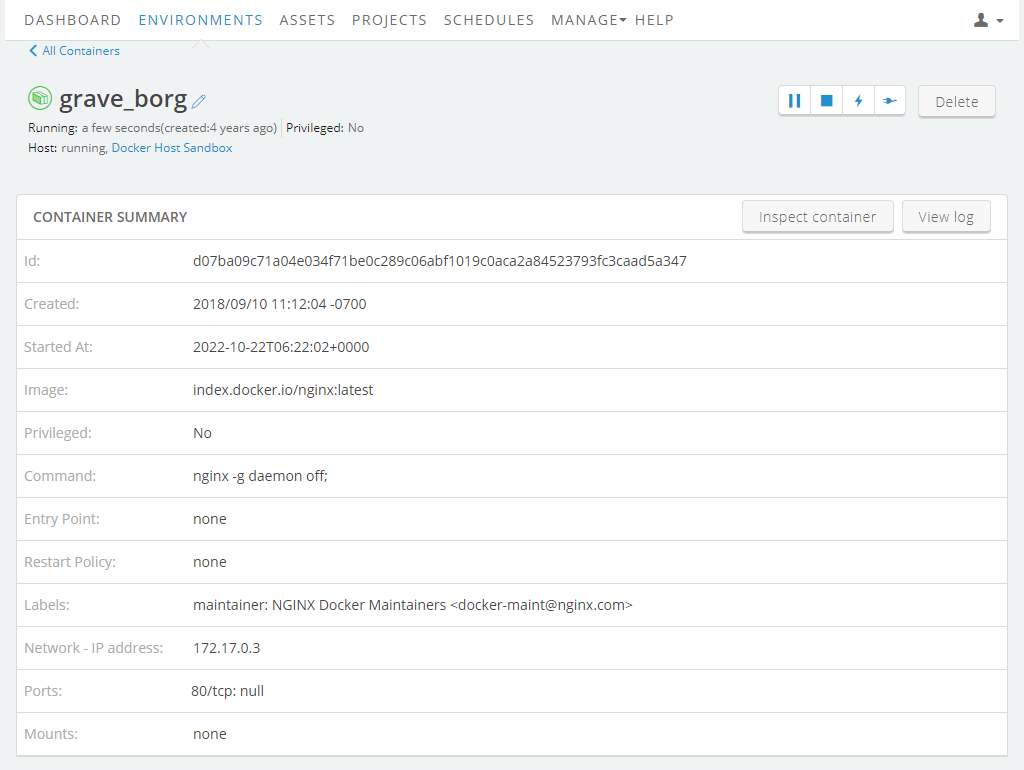
In addition to the run state commands, the following details are displayed for the container:
 (Inspect container) – View the docker inspect report for this container.
(Inspect container) – View the docker inspect report for this container. (View log) – View the most recent entries to the log file for this container.
(View log) – View the most recent entries to the log file for this container.
-
Choose the number of lines to view from the drop-down.
For more information about what information is logged, see docker logs
-
- ID – The full ID of the container.
- Created – The date and time that the container was created.
- Started At – The date and time that the container was last started.
- Image – What image created the container.
- Privileged – Whether this container runs in Privileged mode.
- Command – Arguments fed to the ENTRYPOINT.
- Entry Point – The command that is always executed when this container starts.
- Labels – Docker metadata labels attached to this container.
- Network - IP address – The IP address of this container.
-
Ports – Port bindings for this container.
If you have mapped a host port to this container (see Port mapping), you can connect a Kyndryl Cloud Uplift published service (see Accessing VMs with published services) to this container.
- Mounts – Filesystem mounts for this container.
