Adding a managed DNS name and public IP address to a VM
A public IP address exposes all network ports on the VM, allowing direct inbound and outbound access from the public Internet.
Public IP address access may be disabled by your administrator.
Because there is a greater security risk in exposing a VM to the public Internet, consult your network administrator before using a public IP address. To learn more about other options for sharing a VM with external users, see Accessing VM desktops.
Contents
How to attach a dynamic public IP address with DNS to a VM
To add a managed DNS name and dynamic public IP address to a VM
-
Navigate to the Environment page.
-
From the navigation bar, click Environments. Click the Environments tab.
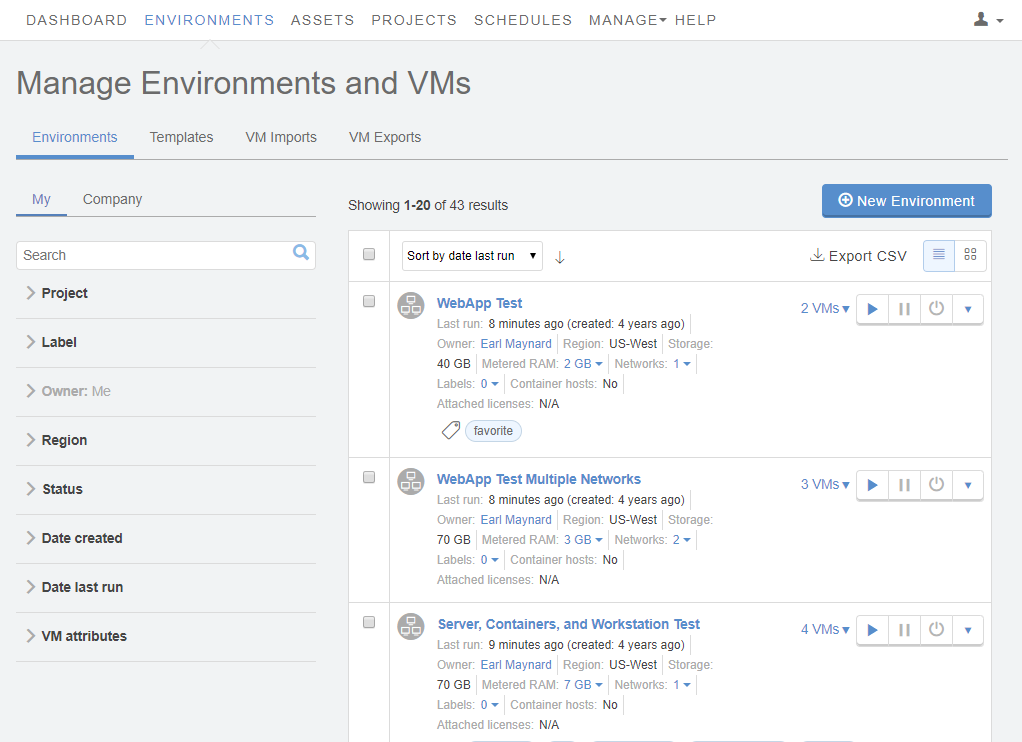
- (Optional) Narrow or sort the list of environments using the filter, search, or sort options.
-
Click the name of the environment.
The Environment Details page displays.
-
-
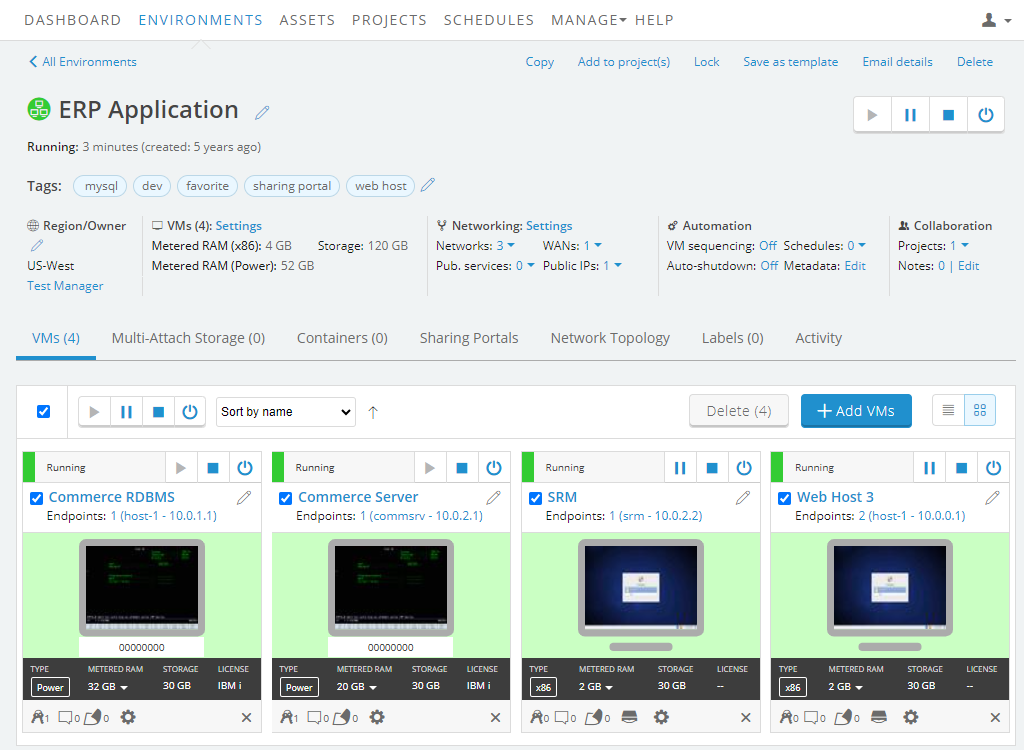
Navigate to the VM Settings > Network Adapters page for the VM you want to edit.
-
Navigate to the environment.

-
Click
 (Settings) for the VM you want to edit.
(Settings) for the VM you want to edit.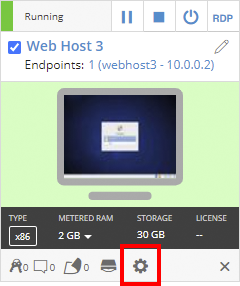
If the Settings button isn’t visible, you don’t have permission to edit the VM settings. Work with your instructor or Kyndryl Cloud Uplift administrator to edit these settings.
-
The VM Settings page displays. Click the Network Adapters tab.
-
-
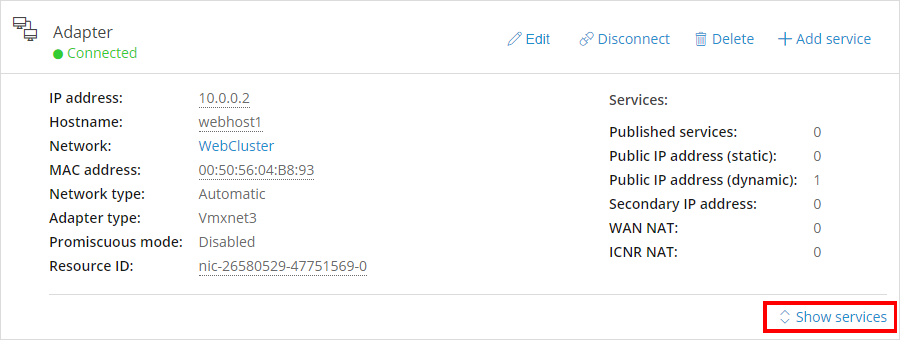
Click
 >
>  .
.Public IP addresses can’t be attached to network adapters on Manual networks. If Add Public IP with DNS is missing, create an automatic network, attach the VM to it, and then repeat the steps above to add the public IP address on the new network adapter.
-
Kyndryl Cloud Uplift automatically:
-
Attaches an available public IP address to the VM (if the VM is running).
This public IP address is subtracted from the remaining number of public IP addresses in your organization’s Kyndryl Cloud Uplift account. Administrators can view and manage these public IP addresses from the Manage Public IP Addresses page.
-
Generates a DNS name for the VM. It may take several minutes for the DNS name to fully propagate.
- For more information, see How does Kyndryl Cloud Uplift generate the VM DNS name?
- To edit the DNS name, see Editing a Kyndryl Cloud Uplift-managed VM DNS name.
If the VM is suspended or powered off, Kyndryl Cloud Uplift generates the DNS name but doesn’t attach a public IP address. The next time the VM is run, an available public IP address will be automatically attached to the VM. The DNS name isn’t accessible unless the VM is running.
-
-
You may need to configure the VM guest OS to accept incoming connections. A guest OS typically has a software-based firewall that blocks most connections to a VM by default. You may not be able to connect to the VM from the public Internet unless you change the firewall rules to allow incoming connections.
- For information about configuring firewall rules for your guest OS, see the guest OS documentation.
- For information about Windows Firewall Rules, see Understanding Firewall Rules and Configuring Firewall Rules.
Also see Protecting a VM that is exposed to the internet or compromised.
Accessing the VM via its DNS name and/or dynamic public IP address
When the VM is running, it’s accessible from the public Internet via the DNS name listed on the network adapter page. It can also be accessed via the dynamic public IP address, though this public IP address is very likely to change the next time the VM is run.
Notes about connecting to the public IP address from:
- Within the VM
Kyndryl Cloud Uplift routes traffic from the public IP address to the VM local IP address via Network Address Translation (NAT). Within the VM, the public IP isn't visible to the guest OS or applications running on the VM. For example, if you're logged into a firewall appliance VM that is attached to a public IP address, you'll need to access the appliance's web interface from the VM local IP address (example: 10.0.0.1).
- Other VMs in the same environment
Generally, a VM can't ping a public IP address that is attached to another VM in the same environment. VMs on the same network must communicate with one another using their private network IP addresses. For more information, see Can I connect to a public IP address or published service from another VM in the same environment?
FAQs
Can I attach a public IP address to a VM that is also connected to a VPN or Virtual Private Network?
Yes. Public IP addresses can be added to an environment that is connected to a VPN or Virtual Private Network (WAN). You should exercise caution to prevent security issues from exposing the environment and WAN to the public Internet.
Related links: Managing VPNs and Private Network Connections, Exposing and blocking public internet access, Protecting a VM that is exposed to the internet or compromised, and Managing public IP addresses.
What happens when I save the VM in a template?
Kyndryl Cloud Uplift automatically generates a unique domain name for each new VM created from the template. When the new VM is run, Kyndryl Cloud Uplift automatically deploys an available public IP address.
See also
- What is the difference between static public IPs and dynamic public IPs with DNS?
- Editing a Kyndryl Cloud Uplift-managed VM DNS name
- Detaching a static public IP address or Kyndryl Cloud Uplift-managed DNS name from a VM
- Troubleshooting issues connecting to a VM via a public IP address or Kyndryl Cloud Uplift-managed DNS name
